When it comes to version control in software development, GitFlow has long been the go-to branching model for many teams. But, there’s a new kid on the block that’s gaining popularity - Trunk Based Development (TBD). In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of TBD and how it can improve your team’s workflow.
Trunk Based Development Workflows
Trunk Based Development is a software development methodology that relies on a single branch (often called the “trunk”) for all development work. Developers integrate their changes frequently into the main codebase, and the codebase is always deployable. Continuous integration and deployment tools are used to ensure that the codebase is stable and ready for production at all times.
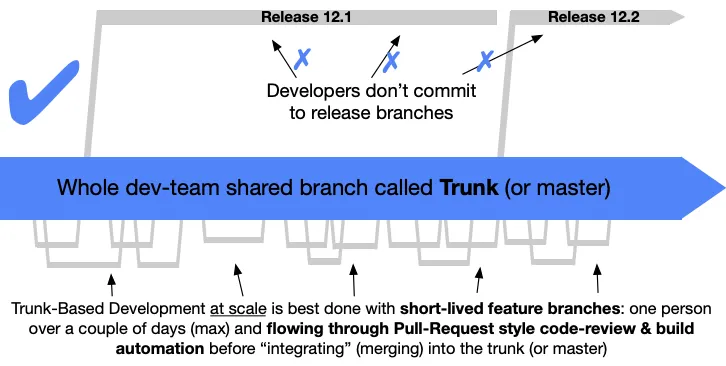
TBD is preferable over GitFlow and other branching models that have multiple long running branches. While it might seem counterintuitive to work on a single branch, TBD has numerous benefits that can streamline your development process and improve code quality.
Pros and Cons
Pros of Trunk Based Development
- Encourages small and frequent code changes, which can improve code quality and reduce the risk of merge conflicts.
- Provides a single source of truth for the codebase, which can improve visibility and collaboration among team members.
- Facilitates continuous integration and testing, which can improve code quality and reduce the risk of bugs and regressions.
- Promotes faster feedback loops and shorter development cycles, which can improve agility and time-to-market.
- Can reduce the overhead of managing multiple long-running branches, which can simplify the development process.
Cons of Trunk Based Development
- Requires a strong testing culture and infrastructure to ensure that changes to the main branch do not break the build or cause issues.
- May be challenging for larger teams where merging changes into the main branch may become more time-consuming.
- May require more frequent deployments, which can be challenging for teams that do not have a robust deployment process or infrastructure in place.
- May require more communication and coordination among team members, which can be challenging for teams that do not have good communication and collaboration practices in place.
- May be harder to maintain backward compatibility with older versions of the codebase, which can be challenging for teams that need to support multiple versions of their software.
Branching
In TBD, there are several types of branches that developers use to manage their work:
main/ormaster/branch is the trunk branch that holds the latest production-ready code.feature/,bugfix/,hotfix/, andadhoc/branches are used for feature development, bug fixing, urgent hotfixes, and ad-hoc changes, respectively.
MR Process
When developers work on a feature or bug fix, they create a new branch from the trunk branch, make the required changes, and ensure to pull changes from the trunk. Once they have completed their work, they create a Merge Request (MR) that will run end-to-end and dev environment deployment. If the pipeline runs successfully, merging the changes into the trunk branch is allowed. After merging, the team can deploy the latest code changes to different environments.
Releases
When it’s time to cut a release, TBD provides a straightforward process. Post-MR, all the latest code changes will be on the trunk branch. The team will cut a release branch as release/ or release- that will be tracked to deploy from dev, pre-prod, prod. No commits should be made on the release branch, and if there are no bug fixes, the same branch can be promoted to prod.
Bug Catching
Catching bugs early and often is essential in TBD. To address this, developers can replicate the issue by creating a bugfix/ branch from the trunk, replicating, fixing the issue, and merging it into the trunk through an MR. Post-MR, the team creates a release branch as release/ or release- to track to deploy.
If the issue cannot be replicated after the fix, the team can cherry-pick the fix commits and put them in the release/ or release- branch (hot fixing).
Conclusion
Trunk Based Development is a simple yet powerful methodology that can help teams deliver high-quality code quickly and efficiently. By relying on a single branch and frequent integrations, TBD provides a streamlined workflow that promotes collaboration, reduces complexity, and catches bugs early. With these benefits in mind, it’s worth considering if Trunk Based Development is the right workflow for your team.
Resources
- Paul-Hammant. “Trunk Based Development.” Trunk Based Development, https://trunkbaseddevelopment.com/.